Git
Introduction
Git a version control system.
A version control system helps you keep track of:
- All changes to each file.
- Why these changes were made.
- And who made them!
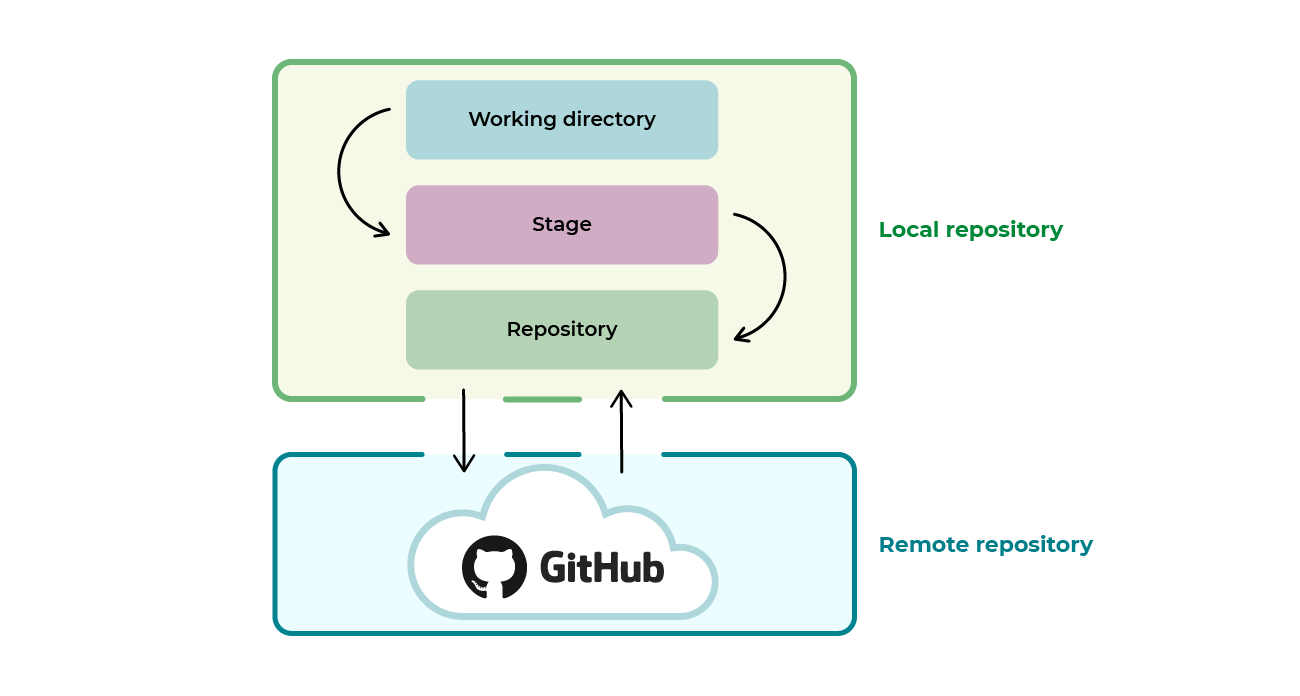
You can use it to create a local repository and manage versions of your files.
First command lines
Create a folder, and initialize a git project in it with the following command:
git init
Create files inside your folder: an index.html and index.css files for example. These will be the files that we will track with git.
Then, stage your files using the following command:
git add —all
Then, create a new version of your git history with the following command:
git commit -m "The commit message"
-m (for message) is what we call an argument, which is added to the main command. In this case, -m allows you to attach a specific message to the commit. If you don’t use the argument, the command “git commit” will open a text editor where you can enter the commit message.
Now you are ready to push your project to a remote repository like github (there are other, like bitbucket or gitlab)!
Additional commands
git status
git branch